What is Kidney Cancer?
Kidney cancer is a malignant cell growth in the kidney (a tumor). The medical name is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors can also be benign.
Kidney cancer is a general term. There are different tumor types and different disease stages in the kidney. Your treatment and experience, will depend on the characteristics of the tumor and the experience of your medical team.
Renal cancers constitute approximately 2% of all cancers diagnosed worldwide. In the last 25 years, the number of kidney cancer patients has increased slightly in Europe. But the survival rate has increased in many regions. Due to advances in imaging technologies such as ultrasound and CT, and more frequent use, more kidney cancer is now diagnosed early.
Men have a higher risk of kidney cancer than women. Most people are diagnosed between 60-70 years of age.
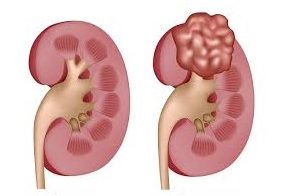
Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer
It is often difficult to determine the causes of kidney cancer. General risk factors include smoking and obesity.
Those with first-degree relative kidney cancer and high blood pressure are also at risk. Some lifestyle changes, most importantly, the quit smoking, the maintenance of healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing kidney cancer.
Symptoms
Böbrek kanseri genellikle asemptomatik olmasına rağmen, 10 kişiden birinde yan ağrısı ve idrar kan gibi belirtiler olabilir. Bu hastalığın ilerlediğinin işareti olabilir. Bazı insanlarda da paraneoplastik sendrom denilen durum görülebilir. Bunlar vücutta oluşan herhangi bir kanser tipi tarafından oluşan ve yüksek kan basıncı, kilo kaybı, ateş, anemi, kas kitlesi kaybı ve iştah kaybı gibi reaksiyonlardır. Böbrek kanseri ile ilişkili sendromlar sıklıkla karaciğer enzimleri ve trombosit değişiklikleri içerir. Bu değişiklikler belirtilere neden olmayıp genelde testler sırasında saptanır.
Kemik ağrısı veya inatçı öksürük kanserin vücudun başka yerlerine de yayıldığının belirtisi olabilir. Bu metastatik hastalık olarak bilinir.
Don't delay, let's meet now !
- Feneryolu Bagdat Avenue No 85/1 Postal Code: 34724 Kadıköy/İstanbul - Turkey
Diagnosis
Because there are different types of kidney tumors, your doctor will perform a number of tests for a better understanding your specific situation. These are medical past and scans. Sometimes a family story is taken. The CT or MRI determines whether the tumor is spread to the local veins, lymph nodes, or surrounding tissues. This is important for further treatments. Blood and urine tests can also be performed near physical examination.
With your scan results, your urologist can define the stage of your disease. By examining the tumor tissue taken during surgery or biopsy, the pathologist determines the subset of tumors and whether they are aggressive. The stage, subgroup and aggressiveness of the tumor constitute the classification.
The classification of the kidney tumor is used to predict the patient-specific prognosis. According to your personal prognosis, your doctor will discuss the best treatment path with you.
In some cases, you may need additional tests for renal function control. This is important if you are at risk of kidney failure due to a single kidney or diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic infection, and kidney disease.
Imaging and classification of kidney tumors is very important. The most common imaging modalities are ultrasound, CT and MRI. In some cases, biopsy is taken to determine the specific characteristics of the tumor.
Treatment
After the diagnosis of localized kidney cancer, your doctor may recommend the treatment of cancer with partial nephrectomy, radical nephrectomy, active surveillance, radiofrequency ablation or cryotherapy. Each process has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of treatment depends on your personal situation.
If you have been diagnosed with locally advanced kidney cancer, your doctor may recommend radical nephrectomy or embolization treatment. Both procedures have their own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of treatment will be determined in relation to your individual situation.
Renal tumors can spread to other organs or lymph nodes. This is called metastatic disease. In metastatic disease, kidney tumors are called primary tumors and tumors in other organs are called metastases. Your doctor may recommend a combination of anti-angiogenic therapy, which is known as the target therapy in the treatment of metastatic disease. In rare cases immunotherapy may be used. Radiotherapy may be recommended for the treatment of metastasis.
Usually, the metastatic disease cannot be cured. Treatment of metastatic disease aims to reduce the size of the primary tumor and metastases. This will give you the chance to live longer and have fewer symptoms.