Erection Problem (Erectile Dysfunction )
Research shows that nearly half of men over the age of 50 experience symptoms of erectile dysfunction (ED). ED becomes more common as men age, but aging alone does not cause ED.
In the past, it was believed that the primary cause of ED was psychological problems (such as stress and anxiety). However, recent studies have shown that in many cases, ED is linked to an underlying organic condition. In this sense, ED may actually be an early warning sign of a more serious problem.
Diagnosing and treating conditions that cause ED is important for both your overall health and your sexual life. With proper treatment, it is possible to maintain a healthy sexual life even in old age.

İçerik
- Erection Problem (Erectile Dysfunction )
- What is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
- How does penile erection occur?
- What are the symptoms of erectile dysfunction?
- What Are the Risk Factors for Erectile Dysfunction?
- Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
- Organic causes
- Psychological Causes
- How is erectile dysfunction diagnosed?
- Treatment Options
- Frequently Asked Questions About Erectile Dysfunction
What is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the most common sexual problem for which men seek medical help. ED is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.
It is not uncommon for a man to experience occasional erectile problems. However, the gradual onset of ED or its occurrence during regular sexual intercourse is not normal and should be treated.
ED can occur in the following situations:
- When blood flow to the penis is limited or nerves are damaged
- Due to stress or emotional causes
- Atherosclerosis (hardening or blockage of the arteries), heart disease, high blood pressure, or high blood sugar caused by diabetes, as an early warning sign of a more serious condition
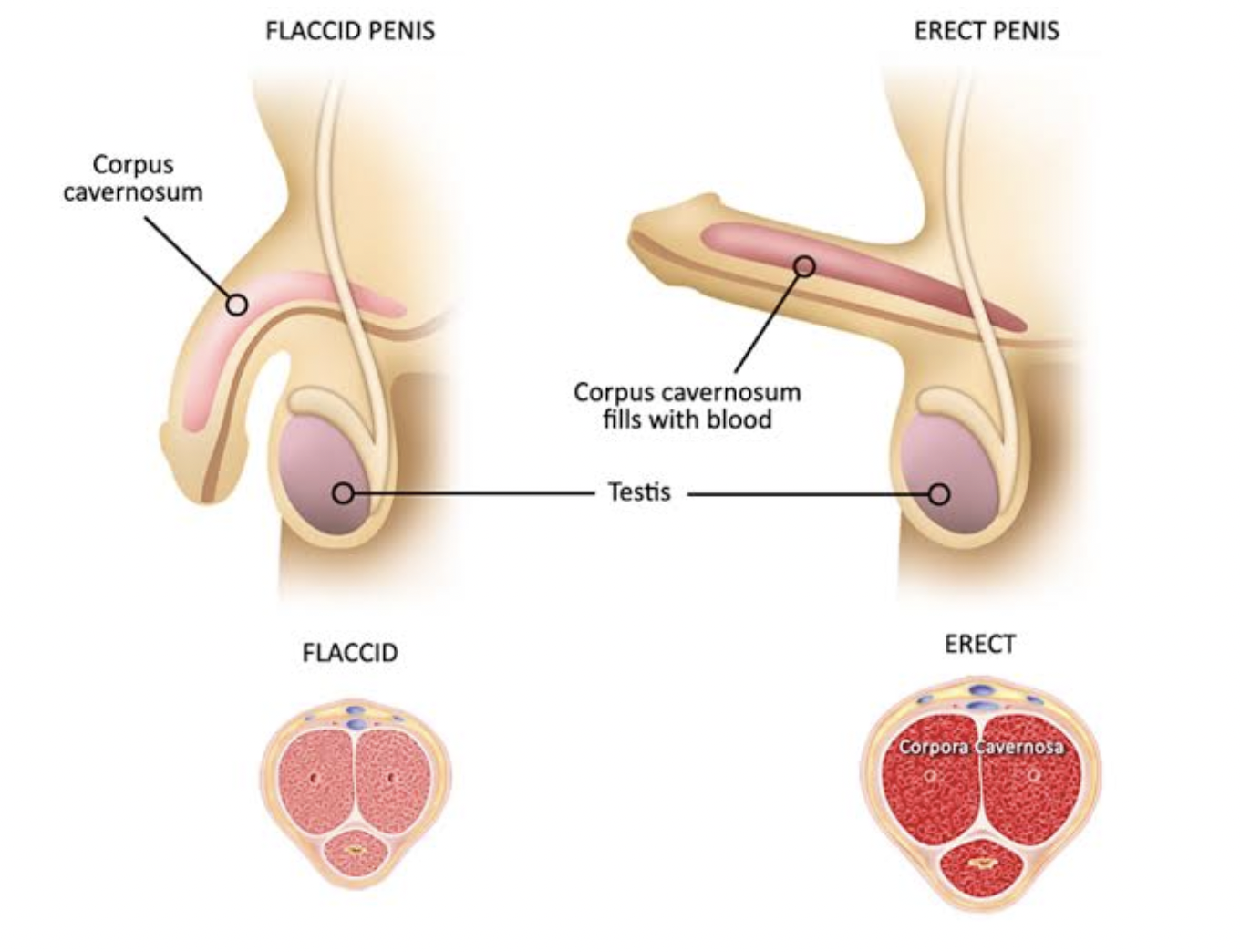
How does penile erection occur?
During sexual arousal, nerves in the brain release chemicals that increase blood flow to the penis. Blood fills two erection chambers called cavernous bodies, which are made up of spongy muscle tissue. The cavernous bodies are not empty; during erection, these spongy tissues relax and trap blood. The pressurized blood inside the cavernous bodies causes the penis to become hard, and an erection occurs.
When a man orgasms, a second set of nerve signals reaches the penis, causing the muscle tissue to contract. This contraction reduces pressure on the collecting vessels, allowing blood to flow back into the circulatory system, and the erection subsides.
When there is no sexual arousal, the penis remains soft and flaccid. Men may notice that the size of the penis changes depending on temperature, cold, or anxiety. This reflects the balance of blood flow entering and leaving the penis and is normal.
What are the symptoms of erectile dysfunction?
Symptoms of ED may include:
- Being able to achieve an erection but not maintaining it long enough to complete sexual intercourse
- Achieving an erection that is not firm enough for sexual intercourse
- Inability to achieve an erection at all
If ED affects your quality of life, you may want to consult a urologist specializing in andrology.
ED can be a major warning sign of cardiovascular disease. It may indicate blockages in the blood vessels in men. Some studies have shown that men with ED have a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, or circulation problems in the legs.
What Are the Risk Factors for Erectile Dysfunction?
Finding the cause of ED will help treat the problem. ED can be caused by organic health problems, emotional issues, or both.
Some known risk factors for ED include:
- Injuries or trauma to the pelvic area (groin or lower abdomen)
- Surgeries for prostate, colon, rectal, or bladder cancer
- Heart disease
- Peripheral artery disease (slowed blood flow due to narrowed arteries)
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar (diabetes)
- Alcohol use
- Drug use
- Smoking or using electronic cigarettes
- Certain medications (e.g., antidepressants, beta blockers, antihypertensives, some antipsychotics, and hormone therapies)
- Emotional stress caused by depression, anxiety, or relationship problems
Although ED becomes more common with age, aging does not always cause ED. Many men in their 80s are able to maintain sexual function.

Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Organic causes
The physical causes of erectile dysfunction (ED) usually stem from conditions that restrict blood flow to the penis or interfere with nerve signals. These conditions include:
- Factors affecting blood vessels or nerves
There are many health issues that can reduce blood flow to the penis.
- Examples:
- Peripheral artery disease or atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Heart disease
- High blood sugar (diabetes)
- Smoking
- Inability of the penis to retain blood during erection
If blood does not remain in the penis, a man cannot maintain an erection. This is often referred to as venous leakage and can occur at any age. - Blockage of nerve signals from the brain or spinal cord to the penis
Certain diseases, spinal cord injuries, or radiation or surgical procedures in the pelvic area can damage the nerves leading to the penis. - Cancer treatments near the pelvic area can affect penis function
Surgery and/or radiation therapy for prostate, colorectal, or bladder cancer can cause ED in men. Patients who have undergone cancer treatment are advised to consult a urologist about sexual health issues. - Some medications used for other health conditions may have adverse effects on erections
Patients should discuss the side effects of their medications with a urologist.
Psychological Causes
Sexual function requires the mind and body to work together. Emotional or relationship problems can trigger or worsen ED.
Emotional issues that may lead to ED include:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Relationship conflicts
- Stress at home or work
- Stress caused by social, cultural, or religious conflicts
- Sexual performance anxiety
How is erectile dysfunction diagnosed?
The diagnosis of erectile dysfunction begins with a consultation with your doctor. Your doctor will ask you some questions about your health and your erection problems. Your doctor may also perform a physical examination and request laboratory tests. Finding the cause of ED is very important in determining the right treatment method.
Medical History
It is very important to talk openly with your doctor. To begin with, your doctor will want to know about your medical history and lifestyle. You will be asked questions about any medications you are taking, your smoking status, alcohol consumption, and any recent stress factors.
Questions about your medical history may include:
- What prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or supplements do you take?
- Do you use any illegal drugs?
- Do you smoke cigarettes or use electronic cigarettes? How much?
- How often do you consume alcohol?
- Have you ever had any surgery or radiation therapy in the pelvic area?
- Do you have any urinary problems?
- Do you have any other health problems (treated or untreated)?
ED History
These questions will help your doctor determine whether your ED is related to sexual desire, erection function, ejaculation, or orgasm. These questions may seem personal, but your doctor is a healthcare professional, and your honest answers will help identify the cause of the problem.
Questions your doctor may ask:
- How long have you been experiencing these symptoms? Did they start gradually or suddenly?
- Do you experience erections in the morning or when you wake up at night?
- How firm are your erections? Is penetration (entry into the vagina) difficult?
- Do you have any problems with sexual desire or arousal?
- Do your erections differ during intercourse, oral stimulation, or masturbation?
- Do you experience pain during erection?
Stress and Psychological Health History
Your doctor may ask you questions about your emotional well-being. They may want to know if you have ever felt depressed or anxious, or if you have had problems in your relationships. Some doctors may also want to talk to your sexual partner.
Questions about your psychological health may include:
- Are you often stressed, or has something happened recently that has been bothering you?
- Is there a situation that is causing you anxiety or depression? Do you have any other mental health issues?
- Are you taking any medications for your mental health?
- How satisfied are you with your sexual life? Have there been any changes recently?
- How is your relationship with your partner? Have you noticed any changes recently?
Physical Examination
An ED evaluation usually begins with an examination of the genital organs (penis and testicles). Depending on your age and risk factors, your heart and circulatory system may also be checked (heart, peripheral pulses, and blood pressure). Depending on your age and family history, a rectal examination may also be performed to check the prostate. These tests are usually painless.
Laboratory Tests
Your doctor may request blood tests and a urine test to check for other health issues that cannot be detected through a physical examination.
Questionnaires
Healthcare professionals may use questionnaires to assess your ED. These questionnaires help determine your ability to initiate and maintain an erection, your satisfaction with sexual intercourse, and any problems with orgasm.
Advanced Erectile Function Tests
In some men, advanced tests may be needed to guide treatment or to evaluate next steps if initial treatment fails. These tests include:
- Blood tests to check testosterone and other male hormones
- Blood tests to measure blood sugar levels (diabetes)
- Checking blood flow with ultrasound (Penile Doppler)
- Injection of a vasodilator medication into the penis
Treatment Options
If erectile dysfunction (ED) is affecting your quality of life or causing difficulties in your relationships, it should be treated. Treatment aims to correct or improve erectile function, support circulatory health, and enhance quality of life.
Don't delay, let's meet now !
- Feneryolu Bagdat Avenue No 85/1 Postal Code: 34724 Kadıköy/İstanbul - Turkey
Lifestyle Changes
ED treatment begins with focusing on your heart and vascular health. Your doctor may identify "risk factors" that can be modified or improved. The following lifestyle changes are encouraged:
- Improving dietary habits (consuming more plant-based foods, limiting fatty and processed foods)
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Increasing physical activity
- Limiting alcohol and drug use
- Getting better sleep (ideally 7–8 hours per night)
Your doctor may recommend adjusting the dosage of your prescription medications. However, you should not stop or change your medications without consulting your doctor.
Emotional Health Care
Your doctor may recommend that you address any emotional issues you are experiencing. These may include relationship conflicts, life stressors, depression, or performance anxiety related to ED. You may wish to ask for a referral to a sexual health counselor or a general mental health counselor. A highly trained professional who can offer evidence-based strategies may be able to help you cope with life's challenges.
Medical Treatments
Non-invasive treatments are typically tried first.
Oral Medications (Oral Treatment)
Some medications that inhibit the PDE type-5 enzyme and are taken by mouth increase blood flow to the penis. These medications are taken orally in pill form.
Oral treatment options approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) include:
- Viagra® e (sildenafil citrate)
- Levitra (® )
- Cialis (® )
- Stendra (® )
For best results, these medications should be taken approximately one to two hours before sexual intercourse. PDE-5 inhibitor medications increase blood flow to help achieve a strong erection. For these medications to be effective, the nerves leading to the penis must be functioning normally. Approximately 70% of men experience improved erections with this treatment. However, response rates may be lower in men with diabetes or cancer.
The most common side effects are generally mild and short-lived:
- Facial flushing
- Headache
- Indigestion
- Muscle aches
- Nasal congestion
Note: If you are taking nitrate medications for heart disease, you should NOT use PDE-5 inhibitors. You must consult your doctor before using these medications.
Vacuum Erection Device (VED)
A vacuum erection device consists of a plastic tube that is placed over the penis, with the end of the tube sealed airtight against the body. A pump at the other end of the tube creates a low-pressure vacuum around the erectile tissues. The pressure created by the pump increases blood flow to the penis, resulting in an erection.
Once an erection is achieved, an elastic ring is placed at the base of the penis to prevent blood from flowing back out. This allows the erection to be maintained for approximately 30 minutes. With proper training, 75 out of every 100 men can achieve a successful erection using a vacuum erection device.
Dietary Supplements
Dietary supplements (also known as herbal remedies) are popular, but they may not be safe or effective. You should consult your doctor before using any supplements to treat ED on your own, as these supplements may contain high doses of PDE-5 inhibitors or unlisted ingredients.
Testosterone Therapy
In some cases, if low sexual desire (libido) and low testosterone levels are detected, testosterone therapy may increase sexual desire. This treatment may help with erections when used in combination with PDE-5 inhibitors.
Intracavernosal (ICI) and Intraurethral (IU) Treatments
If oral medications are ineffective, Alprostadil is an approved medication for men with ED. This medication can be administered via injection into the penis or as a medication pellet placed in the urethra.
Self-injection therapy
The alprostadil-containing medication is injected into the side of the penis using a thin needle. After the injection, erection usually occurs within 20-30 minutes and lasts until ejaculation or the medication wears off. The success rate of ICI therapy is up to 85%.
If alprostadil alone is ineffective or causes pain, different injection medications can be combined. The most common combination is known as Trimix. Trimix is typically mixed at a pharmacy and requires a prescription. The dosage is adjusted based on the severity of ED and your doctor's assessment. If the injection is being administered for the first time, it is important to have it done at a urology clinic to ensure safe administration at home.
Surgical Treatments
The most common surgical treatment for erectile dysfunction is the penile implant (penile prosthesis) procedure. It offers a permanent solution for men who have not benefited from other treatment methods or prefer not to undergo other treatments.
Penile prosthesis treatment:
Penile prostheses are devices that are completely implanted into the body. These devices enable the individual to achieve an erection when desired, allowing for normal and spontaneous sexual intercourse. Although penile prosthesis surgery (like other surgical procedures) carries some risks, the success and satisfaction rates among ED patients are quite high.
There are two types of penile prostheses:
- Semi-Rigid (Bendable) Implants
This is the simplest type of implant. It consists of two bendable rods made of silicone and metal. These rods provide the necessary rigidity for sexual intercourse.
- They can be bent downward for urination.
- They can be positioned upward for sexual intercourse.
- Inflatable Implants
Inflatable implants consist of fluid-filled cylinders placed inside the penis. These cylinders are connected to a pump located in the scrotum. When the pump is activated, the cylinders fill with fluid, causing the penis to become erect.
- Inflatable prostheses provide the most natural-feeling erection and offer a natural sensation for the partner.
- Men can control the degree of firmness and, in some cases, the size of the erection using this implant.
- After inflation, couples can experience immediate intimacy.
What Does the Surgery Process Involve?
Penile implant surgery is performed under anesthesia. Typically, a single small surgical incision is made. This incision:
- The area where the penis meets the abdomen or
- Where the penis meets the scrotum.
No tissue is removed from the penis and blood loss is minimal. Patients may be discharged on the same day or may stay in the hospital overnight.
Penis Prosthesis Surgery Post-Operative Recovery Process:
- Pain may be felt in the first few days after surgery. Your surgeon will recommend medication to alleviate the pain. Additionally, applying ice to the penis can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Pain, bruising, and swelling around the penis may persist for several weeks after surgery.
- Physical activities should be limited for the first month. Your surgeon will explain when and how much exercise you can do during the recovery process.
- Most men can resume sexual activity approximately eight weeks after surgery, but if swelling or pain persists, use of the prosthesis may be delayed. Your surgeon or healthcare professional will show you how to safely inflate and deflate the implant.
Possible Complications After Surgery:
- Initially, there may be bleeding, infection, sensitivity, and pain.
- Over time, a mechanical malfunction may occur in the device. In such cases, part or all of the device may need to be replaced through surgical intervention.
- If an infection develops, the implant may need to be removed. If the penile prosthesis is removed, other non-surgical treatments are generally ineffective.
Innovative Regenerative Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): Uses low-intensity shock waves to repair erectile tissue and restore natural erections.
- Penile Stem Cell Injection: It promotes the regeneration of the smooth muscle tissue known as cavernous tissue, which is responsible for penile erection.
- Exosome Therapy: Penile exosome injection is a new-generation treatment option that provides the healing effects of stem cells without cell transfer, and its mechanism of action is the same as that of stem cell therapy.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injection: This involves injecting serum containing healing growth factors obtained from the patient's own blood using special centrifuge devices into the penile tissue to support tissue regeneration.
